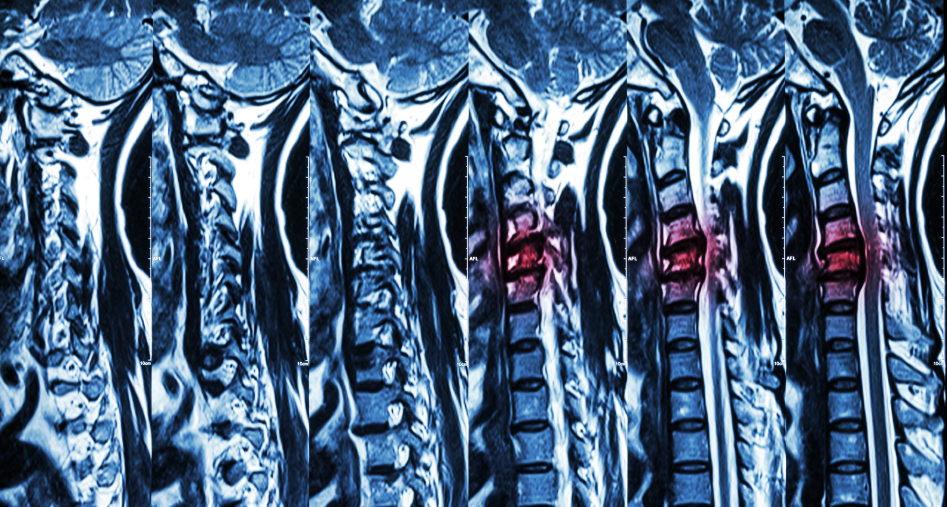
Herniated Disc
Herniated disc refers to a condition in which the disc that sits between vertebrae breaks open and loses its jelly-like substance. This condition affects the back and may not always cause symptoms.
Symptoms that do occur are described as a tingling pain or numbness that may spread down one or both legs.
Tests for herniated discs are not usually offered until symptoms have occurred for at least 4 to 6 weeks.
Tests for herniated discs include imaging scan like MRIs or CT scans that show what is happening with the tissue inside the back.
A physician should be seen if there is:
- New back pain
- Leg weakness
- Problems controlling the bladder or bowels
- “Foot drop” when you can not seem to keep to hold the foot up while walking etc
- Back/leg pain accompanied with a fever
Treatment
- Pain medication
- Muscle relaxants
- Injections
- Spinal manipulation: physical therapist adjusts the back
- Massage
- Keep active
- Surgery: for those with extreme discomfort, surgery involves removing the disc that is injured